How to Drive Rapid Innovation Securely Through Self-Service Cloud Adoption: Scaling at the Speed of Cloud
written by Maya Guevara 8/5/2020
A few weeks ago, we published an article on the importance of company culture in driving secure, yet rapid, innovation in cloud adoption as a part of our “How to Drive Rapid Innovation Securely” series. Based off of the webinar from our founder, Thomas Martin, and Divvy Cloud’s co-founder, Brian Johnson, we will go into more detail how to properly encourage effective and secure innovation using a self-service cloud adoption model — from why a cultural shift is the key ingredient, and how to minimize alert fatigue upon adopting cloud technologies, to the steps to achieve real-time compliance and security remediation.
However, company culture is just the beginning of this conversation. There are many other components that lead to a secure adoption of cloud within company growth, which is why we are delving into the next step in the series: Scaling at the Speed of Cloud.
What is scalability?
Within the context of cloud technologies, scalability is the ability to grow or shrink the size of an IT solution as demanded by the amount of resources available. In addition to the ability to grow or shrink, cloud scalability should have the following key features:
- Noticeable difference
- Relatively fast solutions
- Relatively easy solutions
- Highly customizable yet non-disruptive
There are three main versions of scalability: Vertical, Horizontal and Diagonal.
Vertical scalability helps companies scale up computing requirements by adding more power to existing machines, such as CPU or RAM storage.
On the other hand, horizontal scalability scales out by adding more machines/servers into the cloud architecture.
Finally, diagonal scaling is a mix of horizontal and vertical, which allows businesses to scale accurately to their specific needs.
Why do we need cloud scalability?
Before cloud, companies had to purchase physical server space. This required maintenance, additional/unexpected costs, and distracted businesses from their primary objectives. In addition, purchased server space could not be tailored to the individual needs of each business. Oftentimes, businesses were paying more than they needed for longer than they needed.
With the adoption of cloud, however, comes the ability to pay for only the amount of resources required to run applications as needed — for example, instead of owning a whole server, companies can own a slice of a server. Cloud also introduced a new ability to grow quickly. Whereas companies used to purchase new servers to contain data storage, the cloud removes the physical server limitations and supports business growth as it scales up at its own rate.
The key takeaway within scalability is efficiency. Scalability, whether for a large enterprise or a start-up company, can save both money and time, making it an extremely valuable and necessary investment.
Identifying challenges
A challenge that many companies face is a chasm of knowledge. The traditional way of deploying infrastructure does not align with “how” and “who” deploys infrastructure within the cloud, so the whole process is decentralized from a small set of users in a data center to the company’s broader IT staff.
Additionally, It can be easy to jump into a project too quickly — to see an innovative software and immediately begin implementation. This, however, can be detrimental to a company. When moving too quickly, there is heightened room for failure.
These problems, coupled with the ever growing amount of resources to manage, people touching those resources, and how often those resources are changing, have created a perfect storm and a need to deal with scale.
Overcoming challenges
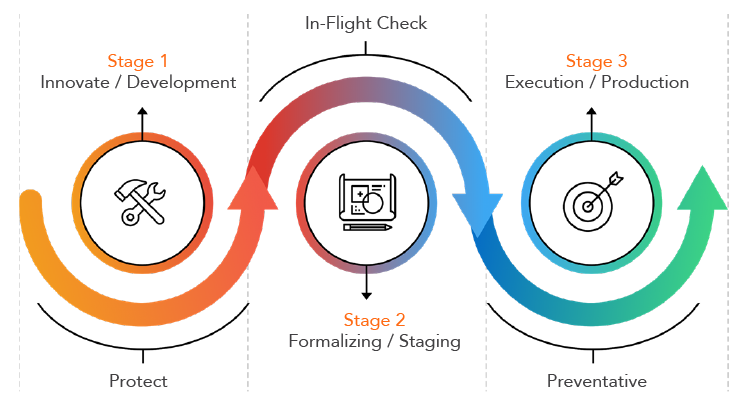
- The first step to scaling at the speed of cloud is internalizing the concept that manual IT processes are complex, time consuming, and simply do not work anymore.
- Next comes training. By taking the time to train engineering organizations about security and deployments, every person who works in cloud based technologies is educated and feels a personal responsibility for maintaining secure and compliant resources.
- Remediation is where the real-time changes come into play. Our strategy using DivvyCloud, there are four main components:
- Harvest – pervasive harvest data using cloud native API endpoints
- Unify – convert infrastructure data into standardized data model
- Analysis – analyze unified data and identify change in cloud infrastructure
- Action – take action and notify, record, and ultimately correct non-compliant resources
- Create holistic strategies and policies. Referring to the image below, prioritizing learning in the development process leads to a more innovative, yet safe, build process.
Need help or have questions? Contact NephōSec at contact@nephosec.com