1. Use a Password Generator / Manager
What is a password generator/manager?
- A password generator is a software program or hardware device that takes input from a random or pseudo-random number generator and automatically generates a password. Random passwords can be generated manually, using simple sources of randomness such as dice or coins, or they can be generated using a computer.
- A password manager will store your login information for all the websites you use and help you log into them automatically. They can also be used to generate strong passwords for you. A password manager will encrypt your password database with a master password – the master password is the only one you have to remember. You can use a password manager to keep track of your generated passwords or to generate them for you.
Why is using a password generator important?
- It is important to use strong passwords as they can help shield against traditional password attacks such as:
- Dictionary – a brute-force technique where attackers run through common words and phrases, such as those from a dictionary, to guess passwords
- Rainbow tables – a precomputed dictionary of plaintext passwords and their corresponding hash values that can be used to find out what plaintext password produces a particular hash (Since more than one text can produce the same hash, it’s not important to know what the original password really was, as long as it produces the same hash.)
- Brute-force attacks – when an attacker attempts to permute through a given character set, where each permutation is checked against the password for a match. Without a timing attack or other vulnerability, this is the most inefficient and computationally intensive way for attempting password retrieval.
What are the risks of using/not using a password generator?
- Weak passwords are still one of the the biggest security risks. Hackers use a multitude of methods to compromise security and gain access to systems. They learn which passwords you use through brute force attacks. When you use weak passwords, you make it easier and faster for hackers to succeed. This is a risk to both user accounts and administrative accounts. Using a password generator not only allows you to have strong passwords, but passwords that are unique to each system and account.
- Using the same password across multiple accounts/systems also increases your exposure and potential data loss if the password becomes compromised. Using a combined generator/manager to keep track of the unique passwords makes this much easier to manage and keeps you more secure.
Here are a few links to for password generators and managers:
You need strong passwords!
A strong password generator tool will help to keep you safe from being attacked online.
2. Install Anti-Virus Software
What is anti-virus software?
-
- Antivirus software is software that is specifically designed to help detect, prevent, and remove malicious software from your computer.
Why is it important to install anti-virus software on your devices?
- Anti-virus software acts like a gatekeeper for your business which checks incoming traffic and blocks unwanted persons from entering. An anti-virus software is crucial for protecting your business and home from malicious software.
Is anti-virus software important for just your desktop & laptops? Or should/can it be installed on all your IoT devices? How do you install anti-virus software on your devices?
-
- Yes! Many IoT devices do support anti-virus software. Remember more and more of our everyday items are becoming part of our IoT.
-
- Make sure your anti-virus is on and patched.
What are some options for anti-virus software?
Remember more and more of our everyday items are becoming part of our IoT!
It is not only our computers, but there are also “things” that interact with the Internet without our intervention. These “things” are continually communicating with the Internet, a fridge sending an update of the food inside or a new exercise gadget.
3. Use a VPN
Who should use a VPN?
- Many employers require the use of a VPN to access company services remotely, for security reasons. A VPN that connects to your office’s server can give you access to internal company networks and resources when you’re not in the office. It can do the same for your home network and while you’re out and about.
- Using a VPN to connect to the internet allows you to surf websites privately and securely. VPNs aren’t just for desktops or laptops — you can also set up a VPN on your iPhone, iPad or Android phone.
When & where should you use a VPN?
- VPNs use encryption to scramble data when it’s sent over a Wi-Fi network. Encryption makes the data unreadable. Data security is especially important when using a public Wi-Fi or other network, because it prevents anyone else on the network from eavesdropping on your internet activity.
Why is using a VPN important?
- VPNs mask your internet protocol (IP) address so your online actions are virtually untraceable. Most important, VPN services establish secure and encrypted connections to provide greater privacy than even a secured Wi-Fi hotspot. VPN’s have the following advantages:
- Privacy – With the VPN, you can surf the internet freely while protecting your identity from exposure. Privacy is vital even as you surf through websites and web apps. There are certain online activities (not fraudulent ones) we usually don’t want to be traced back to us.
- Remote Control and Access – You can use a VPN for a secure remote connection. It’s ideal for businesses because remote access enables their employees to work remotely.
- IP Change – You can keep your IP address hidden as you surf the internet.
What are the risks of not using a VPN?
- No matter where you use your device, you’re at risk of a data breach. Unencrypted data is very vulnerable, as is any info that comes through a browser that isn’t secure. Wireless connections, especially public access points, are particularly vulnerable to sniffers, or computer programs that are used to decode data to make it readable. This includes places that offer free Wi-Fi, such as airports, hotels, and coffee shops. The bad guys use sniffers to spy, steal data, hijack devices, and even steal identities. The good guys use them to determine how secure a network is. Anyone within 30 feet can get all of your data with the right knowledge and tools. They can see everything from your comments on a local news article to your bank account number and password. A VPN can help to protect your computer and your information from sniffers and other types of hacks.
Here is how to get started.
- There are many VPN services for you to use which are both free and paid. Using a VPN is as easy as installing the software on your computer, tablet, or even smartphone and launching the application.
What should you look for in a VPN?
- Security
- Reliable Encryption
- Accessibility
- Ease of Use
- Speed
- Trustworthy
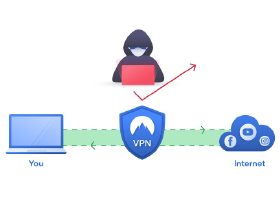
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) connection establishes a secure connection between you and the internet!
Via the VPN, all your data traffic is routed through an encrypted virtual tunnel. This disguises your IP address when you use the internet, making its location invisible to everyone. A VPN connection is also secure against external attacks.
4. Be Careful What You Click On
What are the risks?
- Clicking on a fraudulent link or attachment, may subject you to:
- Phishing – the fraudulent practice of sending emails purporting to be from reputable companies in order to induce individuals to reveal personal information, such as passwords and credit card numbers
- Malware – software that is specifically designed to gain unauthorized access to, disrupt, or damage a computer system
- Ransomware – a type of malware that is a malicious software that infects your computer and/or network of connected devices by encrypting your data. Without the key you will be unable to recover or view your data after which a message is displayed demanding a fee to be paid in order for your system to work again and your data to be unencrypted and readable. This class of malware is a criminal money making scheme that can be installed through deceptive links in an email message, instant message or website.
What to look for and not click on?
- Spotting scam messages is becoming more and more difficult. Many scams can fool experts. However, there are some tricks that criminals will use to try and get you to respond without thinking. Some warning signs include:
- Authority – Is the message claiming to be from someone official? For example, is it from your bank, doctor, or a government department. Criminals often pretend to be important people or companies to trick you into doing what they want.
- Urgency – Are you told you have a limited time to respond (such as ‘within 24 hours’ or ‘immediately’)? Criminals often threaten you with fines or other negative consequences.
- Emotion – Does the message make you panic, fearful, hopeful or curious? Criminals often use threatening language, make false claims of support, or tease you into wanting to find out more.
- Scarcity – Is the message offering something in short supply, like concert tickets, money or a cure for medical conditions? Fear of missing out on a good deal or opportunity can make you respond quickly.
- Current events – Are you expecting to see a message like this? Criminals often exploit current news stories, big events or specific times of year to make their scam seem more relevant.
What are other ways to avoid clicking on something malicious?
-
- The message is sent from a public email domain – look at the email address, not just the sender. No established company will send an email from a public “free” email account. Also be very cautious of emails sent from domains that have a country domain extension versus the traditional .com, .net, .org, etc. Examples include .cn (China) and .ru (Russia).
- The domain name is “spelt” incorrectly.
- The email is poorly written, the email contains grammatical and spelling errors.
- The email includes suspicious attachments or links
- There is a sense of urgency in the email.
How do you check if a link is safe?
- On your computer, you can hover over a link to display it on the bottom of the screen. For iPhones, use haptic touch.
- You can use your browser to check out a site.
- When in doubt, ask your company IT or Information Security staff members.
What do you do if you click on something malicious?
- If it is on your company computer/phone, follow your company policies to report.
- For personal devices:
- Disconnect Your Device – The first thing you need to do is immediately disconnect the compromised device from the Internet.
- Back Up Your Files – Now that you are disconnected from the Internet, you should back up your files. Data can be destroyed or erased in the process of recovering from a phishing attack.
- Scan Your System for Malware – Perform a thorough scan of your system. Run a complete scan with your anti-virus program. Simply follow the program’s instructions to remove or quarantine any suspicious files that are found.
- Change Your Credentials – Malware may be used to harvest sensitive information, including online usernames and passwords, credit card numbers, bank account numbers, and other identifying information.
- Proceed With Caution – Phishing emails have become a dangerous yet unavoidable threat in the digital age. Your best protection is to err on the side of caution and use the “delete” button on emails and text messages that seem sketchy. Remember, a legitimate organization or business will never ask you to share sensitive, personal information via insecure channels like email, text or pop-up messages. If the message is truly important, the sender will attempt to contact you through verified methods like telephone or snail mail.
- Set Up a Fraud Alert – According to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), the FBI reports consumers have lost $57 million in a single year to phishing schemes. To protect yourself, contact one of the major credit bureaus and ask for a free fraud alert to be placed on your credit report.
Can’t say it enough…be careful what you click on!
Emails or text message links and attachments can lead you to ‘look a like’ sites that are intent on stealing your personal information or information about your private accounts. These links or attachments may also download malware or ransomware onto your device or network.
5. Patch Your Router Monthly
What are some of the risks associated with not patching your router regularly?
- Your wireless router functions as a firewall and protects your devices from incoming traffic. If there are security holes in your router it can lead to them being infected by malware and your router could be added to a botnet. A botnet is a number of Internet-connected devices, each of which is running one or more bots. Botnets can be used to perform Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks, steal data, send spam, and allow the attacker to access the device and its connection.
When should you patch your router? How often? Does your provider have automatic patching of your router available and if so, is it set up?
- Unfortunately many companies do not automatically install security updates and their updates require manual installation.
Why is patching your router important?
Your router is your gateway to the internet. As such, it is important to make sure it is secure and does not have vulnerabilities that could allow malicious actors to access your network. Because of this it is important to make sure you have the latest firmware updates which will make sure you have all of the latest security policies and patches from your manufacturer.
6. MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication)
In order to gain access, your credentials must come from at least two different categories. One of the most common methods is to login using your user name and password. Then a unique one-time code will be generated and sent to your phone or email, which you would then enter within the allotted amount of time. This unique code is the second factor.
When should MFA be used?
- MFA should be used to add an additional layer of security around sites containing sensitive information, or whenever enhanced security is desirable. MFA makes it more difficult for unauthorized people to log in as the account holder.
- According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) MFA should be used whenever possible, especially when it comes to your most sensitive data—like your primary email, financial accounts, and health records.
- Some organizations will require you to use MFA; with others it is optional. If you have the option to enable it, you should take the initiative to do so to protect your data and your identity.
How do I activate MFA on my accounts?
- Head to the Lock Down Your Login site, which provides instructions on how to apply this stronger form of security to many common websites and software products you may use.
- If any of your accounts are not listed on that resource site, look at your account settings or user profile and check whether MFA is an available option. If you see it there, consider implementing it right away!
- Usernames and passwords are no longer sufficient to protect accounts with sensitive information. By using multifactor authentication, you can protect these accounts and reduce the risk of online fraud and identity theft.
- Consider also activating this feature on your social media accounts!
MFA is a security process that requires more than one method of authentication from independent sources to verify the user’s unique identity.
There are three categories of credentials:
SOMETHING YOU KNOW
- Password/Passphrase
- PIN Number
SOMETHING YOU HAVE
- Security Token or App
- Verification Text, Call, Email
- Smart Card
SOMETHING YOU ARE
- Fingerprint
- Facial Recognition
- Voice Recognition